The Health Opportunity and Equity Initiative (HOPE)
/"The Health Opportunity and Equity (HOPE) Initiative, funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, was launched to start a new conversation about health because we believe that every person in the U.S., no matter their background or ZIP code, should have a fair and just opportunity for the best possible health and well-being.
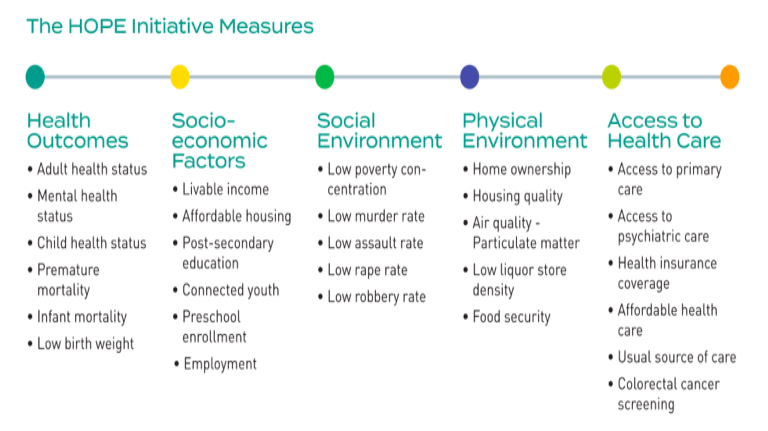
The HOPE Initiative tracks 28 indicators that span the life course, including health outcomes and indicators related to opportunity such as socioeconomic factors, the physical and social environment, and access to health care at the state and national level. Gaps in health do not develop by chance or by choice. These measures were chosen because they reflect the systems and policies that affect health equity. Data are also provided by race, ethnicity and socioeconomic status, making this the first tool of its kind..."
To learn more about Health Opportunity and Equity Initiative, visit the website here.
Read More